Synthetic Fuels as a Lifeline for Combustion Engines
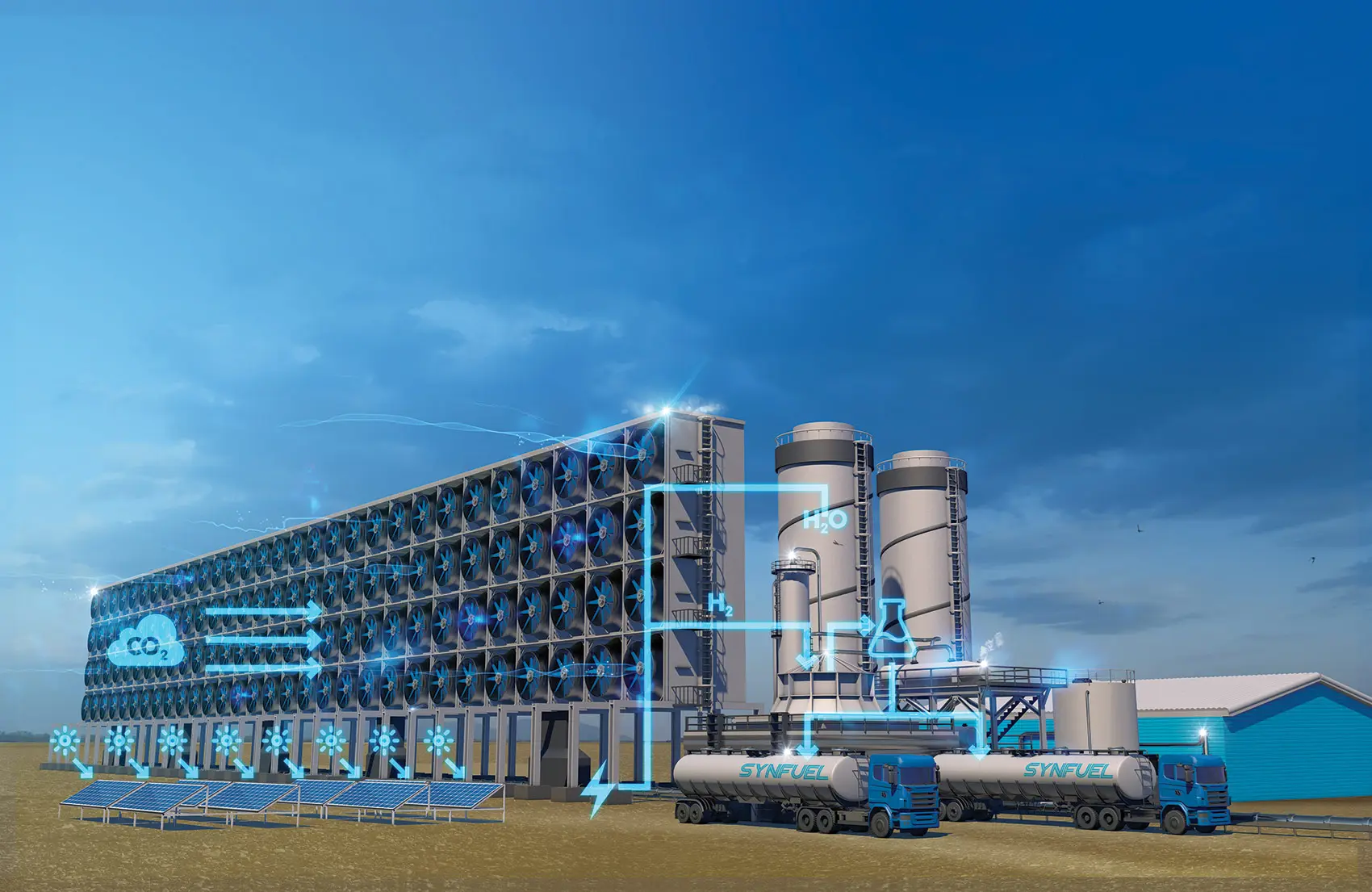

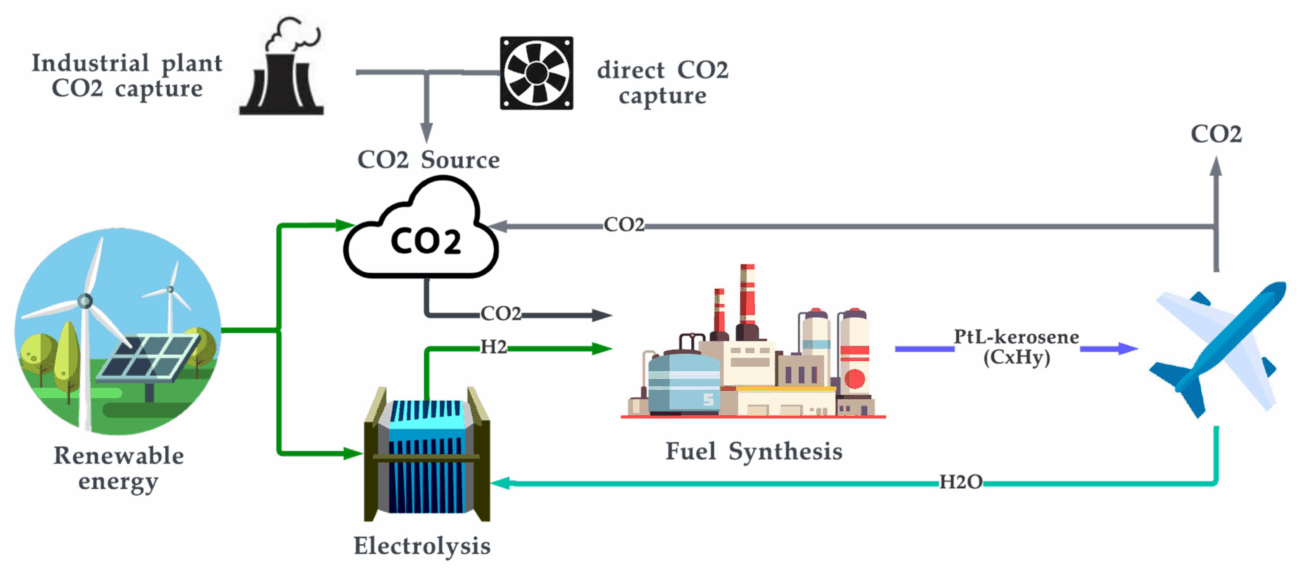
Synthetic fuels, often called “e-fuels,” are gaining attention in 2025 as a carbon-neutral drop-in replacement for petrol and diesel. Made by combining captured CO₂ with green hydrogen through the Fischer–Tropsch or Power‑to‑Liquid process, they release only the CO₂ they stored—netting zero additional emissions on a lifecycle basis.
Major players like Porsche, Lamborghini, and Audi have invested in synthetic fuel projects. Porsche’s Haru Oni pilot plant in Chile has been producing e‑fuel since 2022, even powering a Porsche 911 on a drift demo. Lamborghini’s CTO recently endorsed e-fuels, saying they “could be the savior of the combustion engine,” and designed its new V8 to run seamlessly on both petrol and e-fuel. Learn more on how brand like Lamborghini is researching the use of synthetic fuels.
Even policy is evolving: the EU’s 2035 emissions ban will allow continued sales of ICE vehicles—but only if they run exclusively on CO₂-neutral fuels. Germany and Italy welcomed this, calling it a pragmatic way to preserve their automotive industry.
Real-World Examples and Technological Progress
Porsche’s Haru Oni Pilot in Chile 🔗
Built with wind-powered electrolysis, the Haru Oni plant produces synthetic methanol and gasoline. By 2025, it aims to scale from ~130,000 L per year to hundreds of millions . Early tests—like running a 911 up snowy Chilean slopes—showcase e‑fuels in real-world conditions.
Lamborghini’s V8 e‑fuel Compatibility
In June 2025, Lamborghini confirmed that its new Temerario V8 runs equally well on synthetic fuels. CTO Rouven Mohr emphasized that this technology preserves traditional driving emotion, crucial in the luxury performance segment.
Global Policy and Industry Momentum
- EU Law Adjustment: Regulators allowed a 2035 “e‑fuel exception” for ICE vehicles.
- Corporate Investment: Porsche expects e‑fuels to grow significantly by 2030.
- Aramco’s Entry: Saudi Aramco is building e-fuel plants in Spain and Saudi Arabia, advocating for e-fuels in hybrid ICEs.
Source:
Opportunities and Limitations for Automakers and Drivers
✅ Benefits
- Zero lifecycle CO₂: The CO₂ used in fuel production offsets what is emitted during combustion.
- No New Infrastructure Needed: E-fuels are compatible with existing ICE vehicles and filling stations.
- Preserves Automotive Legacy: High-end brands can maintain signature engine experiences using familiar tech.
⚠️ Challenges
- High Cost & Energy Demand: At ~$14/gallon, production remains expensive and energy-intensive.
- Production Scale: Current plants produce thousands of litres—not enough for mass adoption.
- Efficiency Debate: Critics argue it’s more efficient to use that electricity for EVs, which drive further on the same energy.
